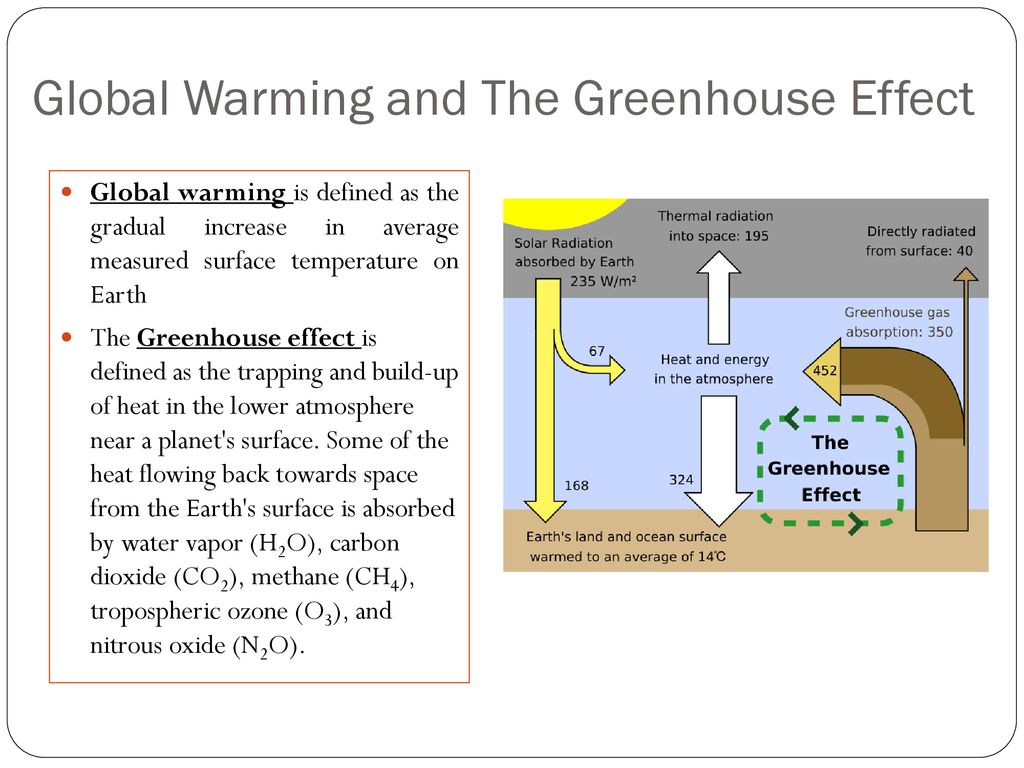
The use of a glass greenhouse to illustrate the greenhouse effect is only appropriate at a coarse "end result" level, not as an actual model of how the CO2induced GHE actually works But in any case, the sunlight entering a (glass) greenhouse warms all dark surfaces within the space (floor, plant leaves, whatever)Greenhouse effect A term used to describe the heating of the atmosphere owing to the presence of carbon dioxide and other gas es Without the presence of these gases, heat from the sun would return to space in the form of infrared radiationCHAPTER 7 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT We examine in this chapter the role played by atmospheric gases in controlling the temperature of the Earth The main source of heat to the Earth is solar energy, which is transmitted from the Sun to the Earth by radiation and is converted to heat at the Earth's surface

Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse effect definition biology quizlet
Greenhouse effect definition biology quizlet-Nowadays we hear a lot about the "greenhouse effect" because the Earth is warm and it is some gases in the air (greenhouse gases) that are responsible for keeping the Earth warm and suitable for life as we know it Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm



Www Extension Purdue Edu Extmedia Id Id 506 W Pdf
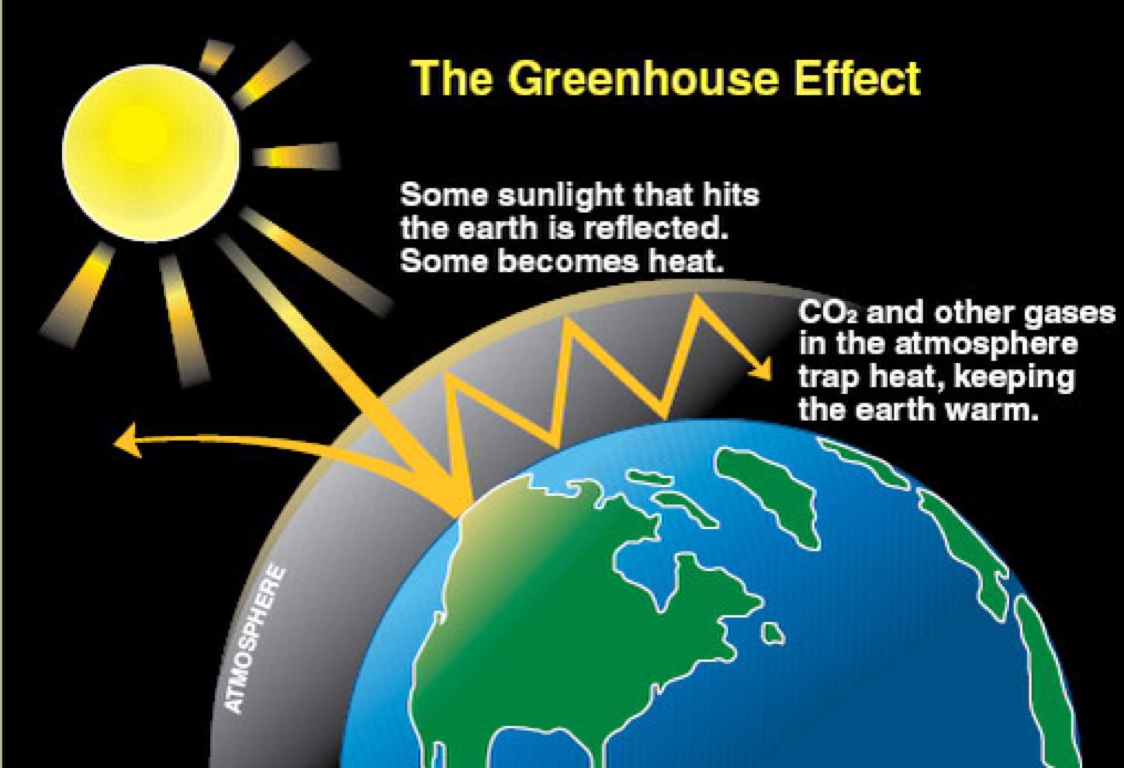
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Define greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth Some heat is reflected back through the atmosphere, while some is The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth an increase in the earth's atmospheric and oceanic temperatures widely predicted to occur due to an increase in the greenhouse effect resulting especially from pollution A Russianowned tanker, built to traverse the frozen waters of the Arctic, completed a journey in record time from Europe to Asia this month, auguring the future of shipping as global warming melts sea iceThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works
In this lab, you will further your understanding of the Earth's energy balance that you investigated in the previous labs First, watch the narrated video, describing the importance of the greenhouse effect in making the planet habitable, or able to support life After viewing the video, discuss the question listed below with your classmates5 human impacts on the environment This is the currently selected itemLess trees > less photosynthesis > more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere > enhances the greenhouse effect Habitat destruction and reduced biodiversity Limits food and space Displaces animals creating more conflict with humans and increased proximity increasing chance of zoonotic disease Impact increased if keystone species affected



1




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet
Definition ear co COA "SRS ear Q Draw and label figure 39 (Pg 87) b 11 We"/ reæn ÐuS oases 2144k" 3 va/or O Solar Energy the Greenhouse Effect Draw and label graph' ere The Gre house Effect on Earth Suth Draw and label graphic here Latitude and Solar Energy Make the notes into a Quizlet or flash cards Make the vocabularyBiology Chapter 4 Climate Flashcards Quizlet Biology I Ch 4 Climate STUDY PLAY weather he condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place climate the weather in a specific area averaged over a long period of time greenhouse effect warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere habitatGreenhouse effect The process of energy absorption and reradiation by the GHGs in the atmosphere Background Information To understand the role of greenhouse gases in global climate change, it is important to understand the basics of blackbody radiation and the interaction of greenhouse gases with Earth's longwave radiation




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse Effect 101 By increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, we're amplifying the planet's natural greenhouse effect andModern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the socalled greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and other greenhouse gasesThe greenhouse effect definition 1 an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere (= mixture of Learn more



Greenhouse Effect Definition Biology ちょうど最高の引用




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Definition of greenhouse effect warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back toIn a specific area averaged over a long period of time greenhouse effect warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere habitat Biology I Ch 4 Climate Flashcards Quizlet Study Biology Chapter 4 Section 1 The Role of Climate Flashcards at ProProfs Biology Chapter 4 Section 1 The Role of Climate




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet
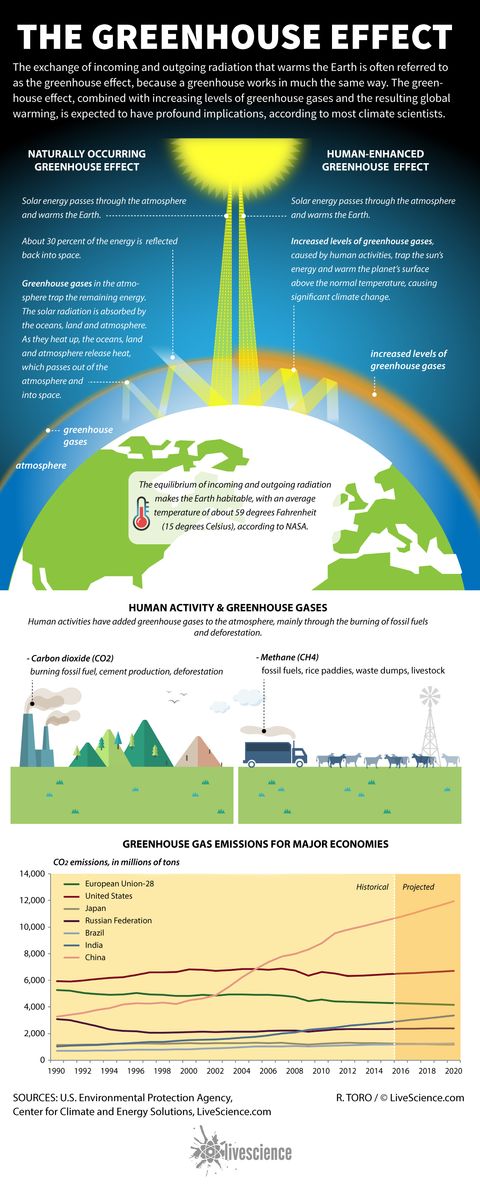
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trapCommunity ecology Feel the love Community ecology II Predators Ecological succession Change is good Ecosystem ecology Links in the chain The hydrologic and carbon cycles Always recycle!The increased greenhouse effect is causing changes in our planet that can affect our lives The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide




Greenhouse Gases Good Or Bad National Geographic Society




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse effect is nothing but the process by which radiation from the planet's atmosphere warms up its surface to a temperature above the atmospheric level The thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directionsThe greenhouse effect Another group of greenhouse gases includes the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFCs have been responsible for depleting theA natural function of the Earth's atmosphere is to keep in some of the heat that is lost from the Earth This is known as the greenhouse effect The atmosphere allows the heat from the Sun




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet



Ess Topic 7 3 Climate Change Mitigation And Adaptation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
SECTION 191 REVIEW ECOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms 1 ecology 2 greenhouse effect 3 biosphere 4 ecosystem 5 community 6 population MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank 1 What percentage of the world's species are expected to disappear in the next century if the current rate of extinction continues?Greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases areGreenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees Celsius



1




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect and climate change Effects of climatic change Resources The greenhouse effect is the retention by Earth ' s atmosphere in the form of heat some of the energy that arrives from the sun as light Certain gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are transparent to most of the wavelengthsThe strength of CFC absorption bands and the unique susceptibility of the atmosphere at wavelengths where CFCs (indeed all covalent fluorine compounds) absorb creates a "super" greenhouse effect from CFCs and other unreactive fluorinecontaining gases such as perfluorocarbons, HFCs, HCFCs, bromofluorocarbons, SF 6, and NF 3 Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Global Warming And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse effect Methane (CH4) Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosph a glass building in which plants are grown that need protectio A change that is a result or consequence of an action or other A gas produced by bacteria from hydrogen and carbon dioxide greenhouse effectThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic




Chapter 16 Flashcards Quizlet
An increase in the earth's average atmospheric temperature that causes corresponding changes in climate and that may result from the greenhouse effectNitrogen and phosphorus cycles Always recycle! The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the



Www Extension Purdue Edu Extmedia Id Id 506 W Pdf



The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet
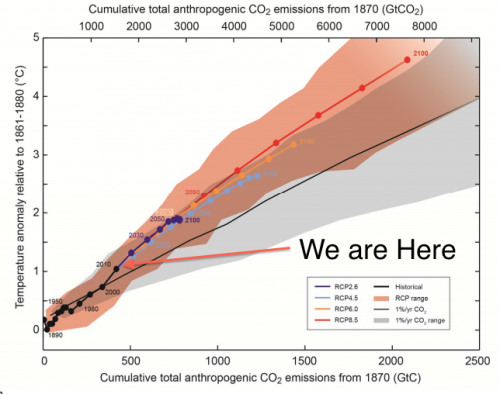
To make or build substances such as sugar and protein within t The movement of substances into and around the organism Release of waste products from Metabolism into the environment Maintaining internal balance such as temperature and waterGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16° F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly



How Does The Greenhouse Effect Work Quizlet




Geography Test 1 The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Ch 7 Biology Flash Cards Flashcards Quizlet



The Greenhouse Effect



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Which Of The Following Activities Decreases Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere A Cutting Down Trees B Driving Gasoline Powered Vehicles C Using Electricity From Coal Powered Plants D Planting Trees E Heating Your
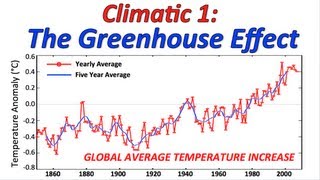



4 4 Climate Change Bioknowledgy




Best Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse What Is A Conservatory




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet
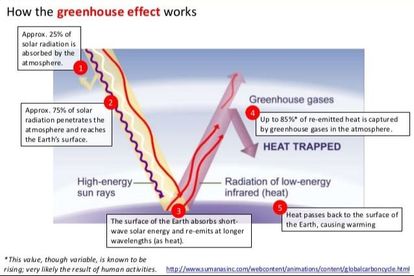



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
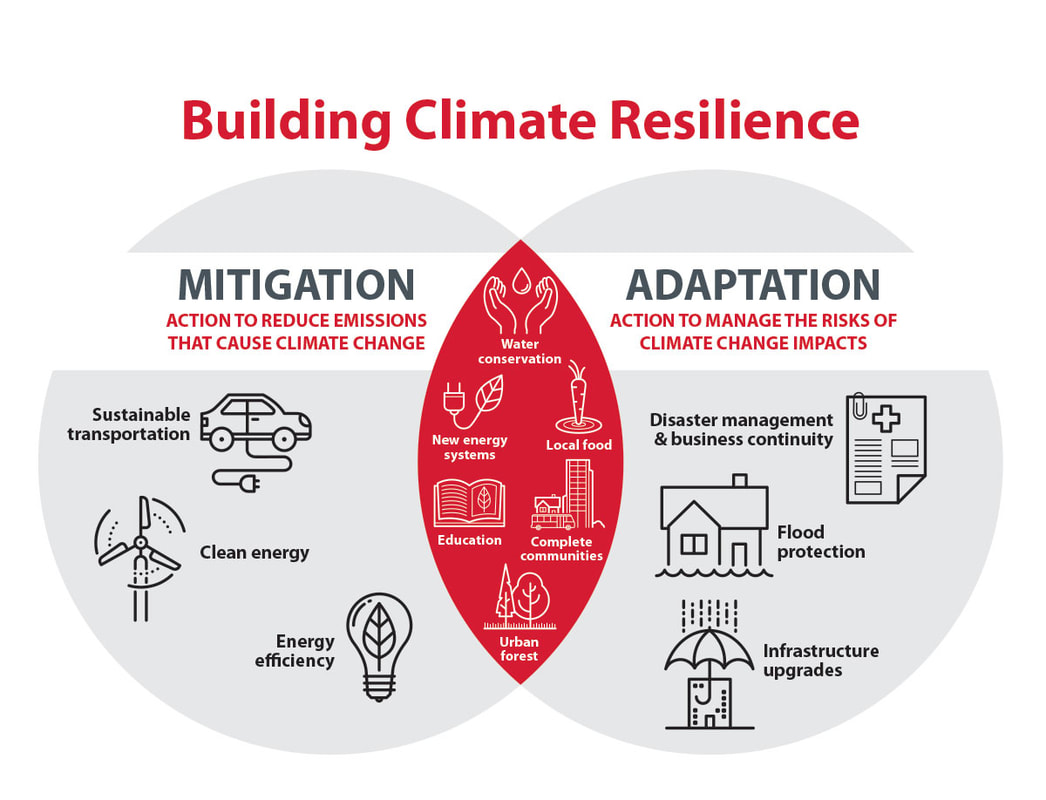



Ess Topic 7 3 Climate Change Mitigation And Adaptation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet
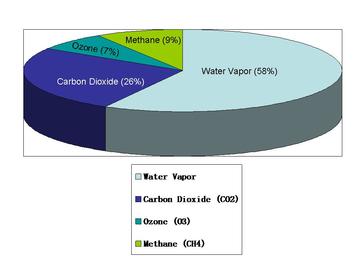



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
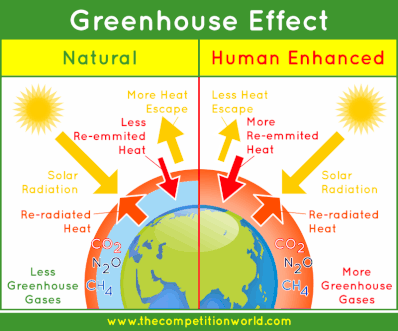



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




4 4 Climate Change Bioknowledgy




Best Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse What Is A Conservatory




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




What Is The Significance Of The Montreal Protocol Quizlet




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




How Does The Greenhouse Effect Work Quizlet




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




4 4 Climate Change Bioknowledgy
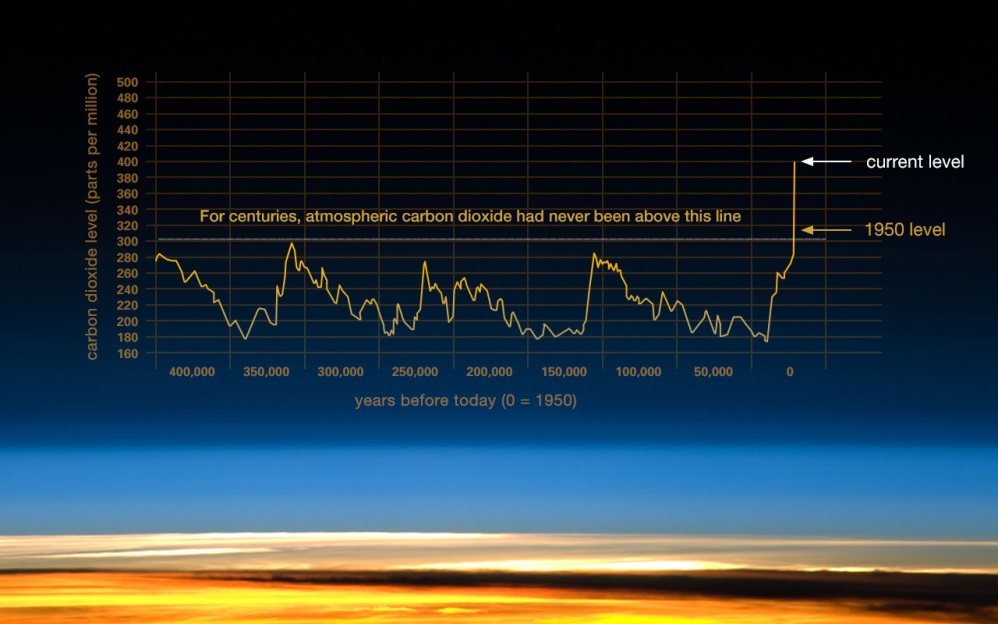



Causes And Greenhouse Effect



1
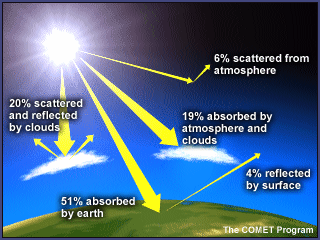



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
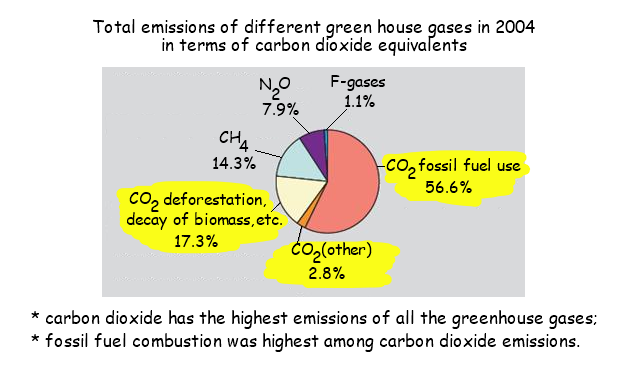



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet



Www Extension Purdue Edu Extmedia Id Id 506 W Pdf



Greenhouse Effect Definition Biology ちょうど最高の引用
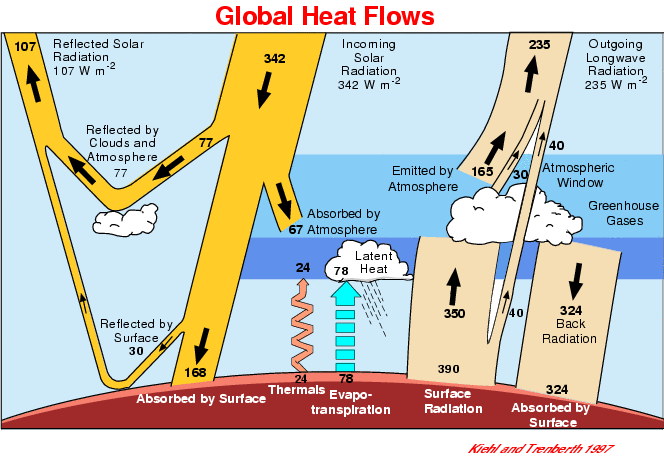



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science
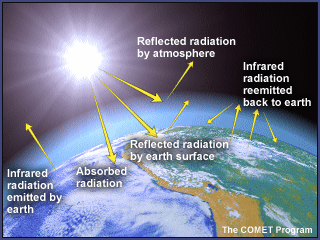



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet



Greenhouse Effect Lincoln University




Apes Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Ozone Layer Flashcards Quizlet




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet
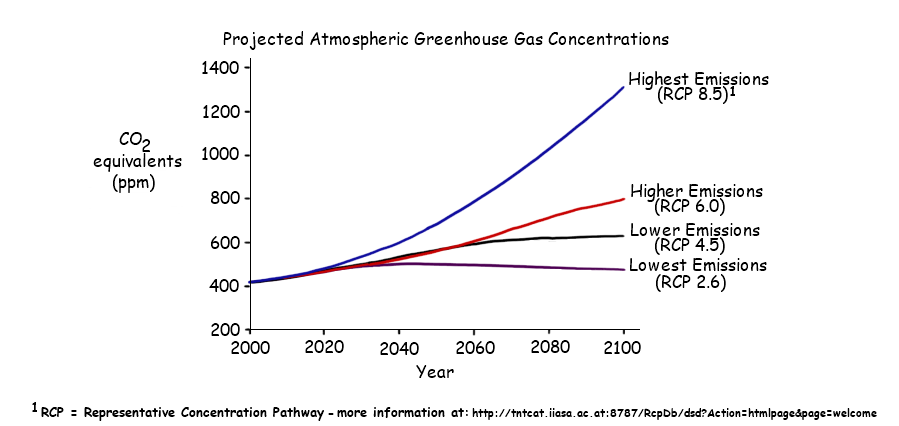



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet



How Does The Greenhouse Effect Work Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Definition Biology ちょうど最高の引用




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect 1 Flashcards Quizlet
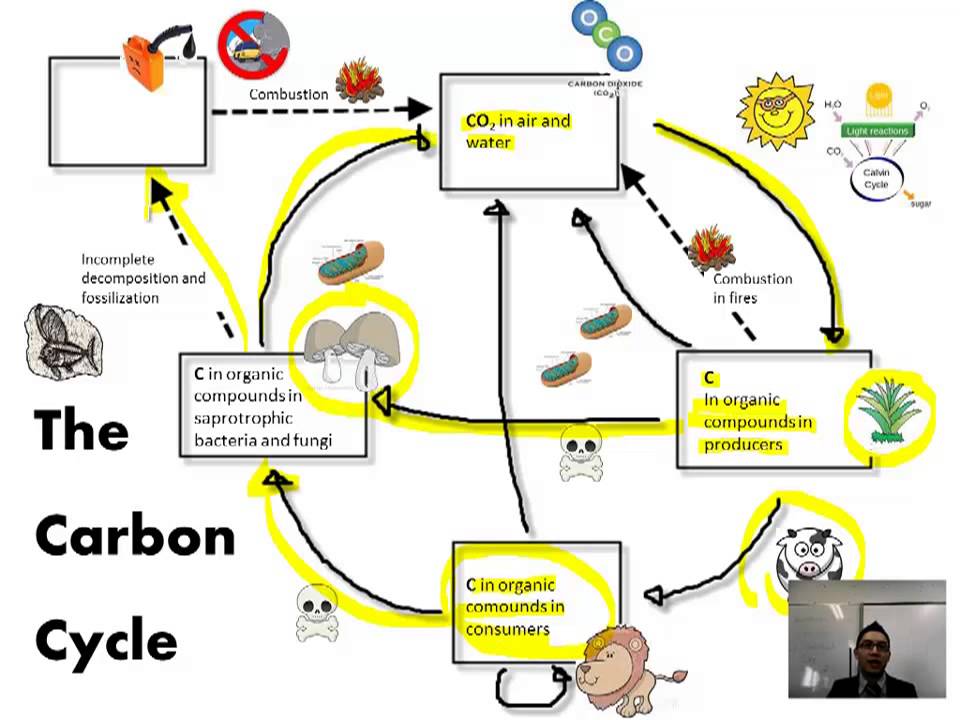



The Greenhouse Effect Ib Biology Youtube




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Biology And Life Science Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




Climate And The Carbon Cycle Unit Overview



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Diagram Quizlet



6 A Simplified Diagram Illustrating The Greenhouse Effect Based On A Download Scientific Diagram




The Diagram Below Shows A Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Which Would Happen More If There Were No Brainly Com
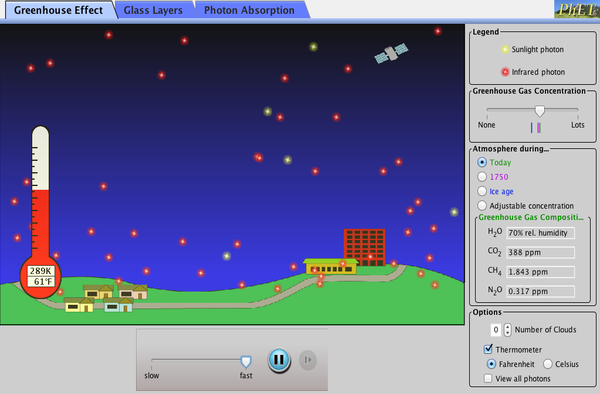



The Greenhouse Effect




11 The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




4 4 Climate Change Bioknowledgy



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Definition Biology ちょうど最高の引用




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Kyoto Protocol History Provisions Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Worksheets Teaching Resources Tpt




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources




The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿