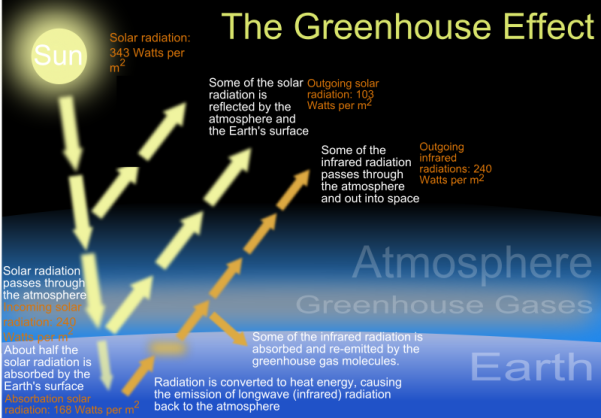
15/7/21 The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxidesThe greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space A simplified diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect (based on a figure in the 07 IPCCAnd necessary pathways which are compatible with limiting warming to 15°C or 2°C of warming this century 14

Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram-5/7/21 These greenhouse gases absorb heat radiated from the Earth then release energy in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more details about thisGreenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time




Climate Greenhouse Gases Sustainability
CHAPTER 7 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT We examine in this chapter the role played by atmospheric gases in controlling the temperature of the Earth The main source of heat to the Earth is solar energy, which is transmitted from the Sun to the Earth by radiation and is converted to heat at the Earth's surfaceHuman activities have led to a build up of extra greenhouse gases in the atmsophere;If all countries achieved their current future pledges for emissions reductions;
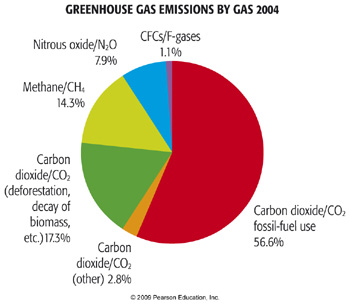
13/5/06 A greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gasesThis is called the "greenhouse effect"Most greenhouse gases are natural water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth Other greenhouse gasesGreenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today farGreenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is reradiated in all directions Since part of this reradiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperature above
16/7/21 The issue of greenhouse gas emissions is evidently a serious one The damage we humans have caused is already at a critical point, and without some serious interventions, the future is looking bleak However, by learning about the impacts of the greenhouse effect and climate change, we can start to take steps to correct it"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau
As a result, average surface temperatures are rising14/8/ Greenhouse gas, any gas capable of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gasesIf current policies continued;
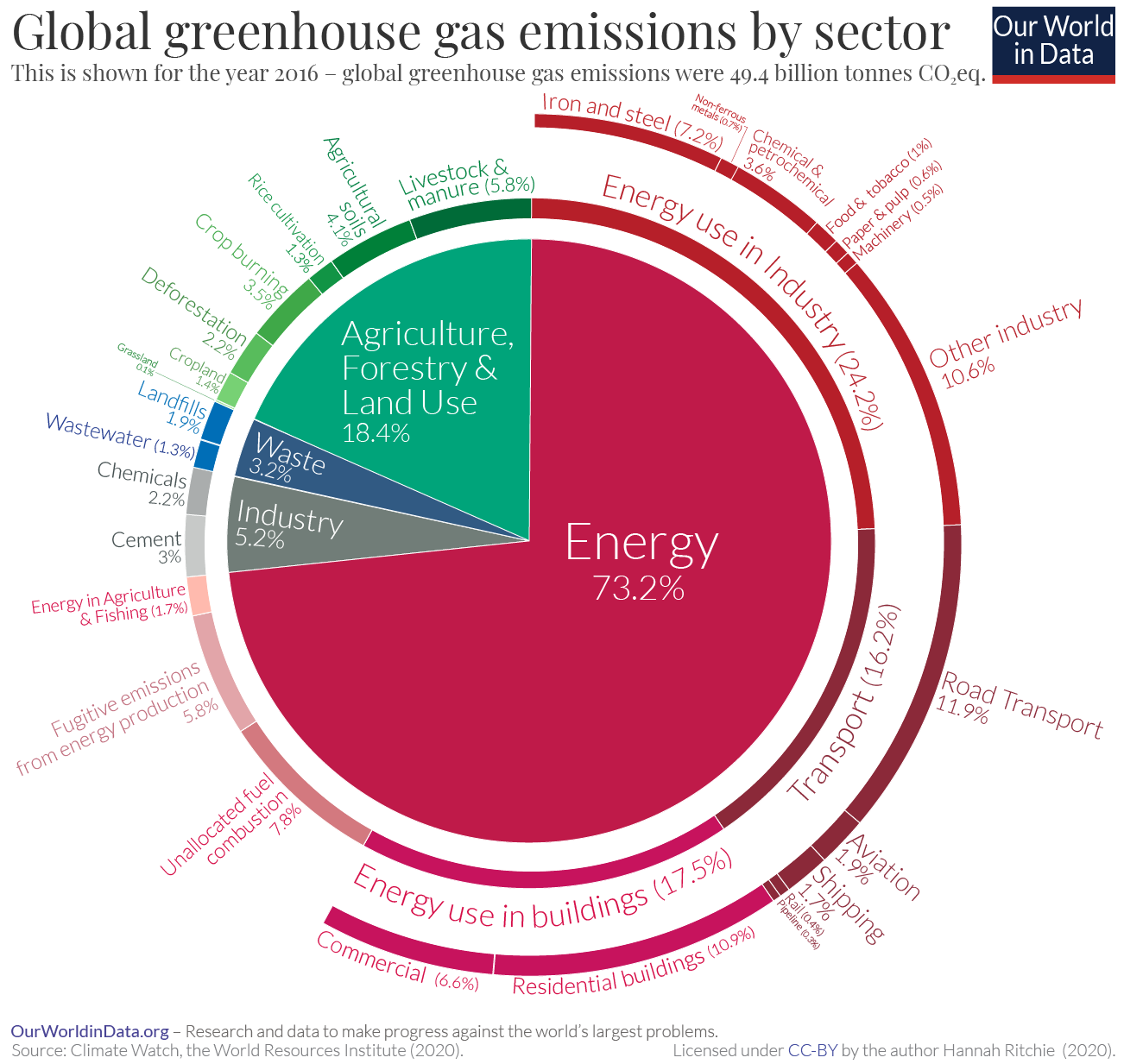



Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times
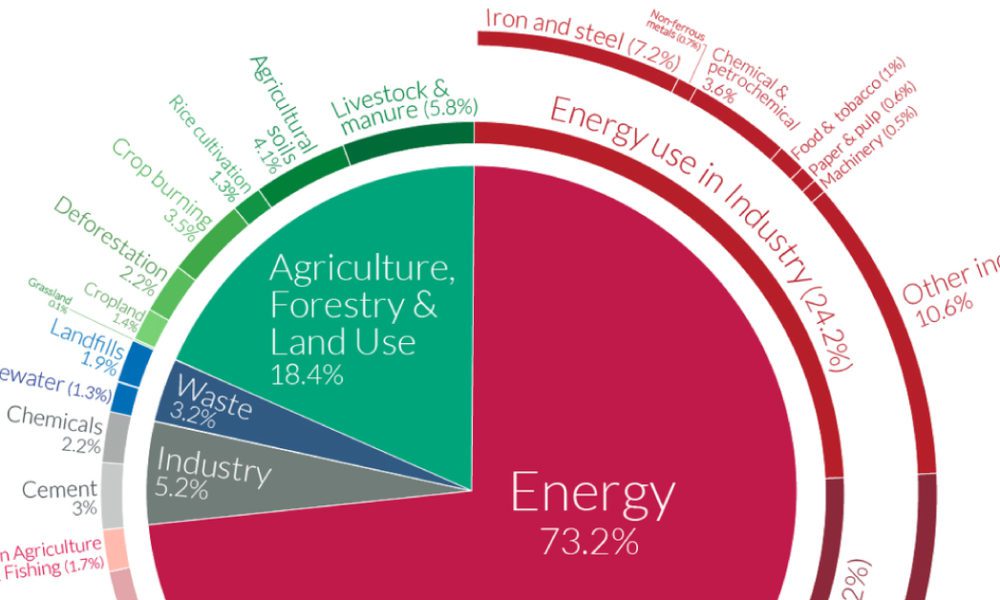
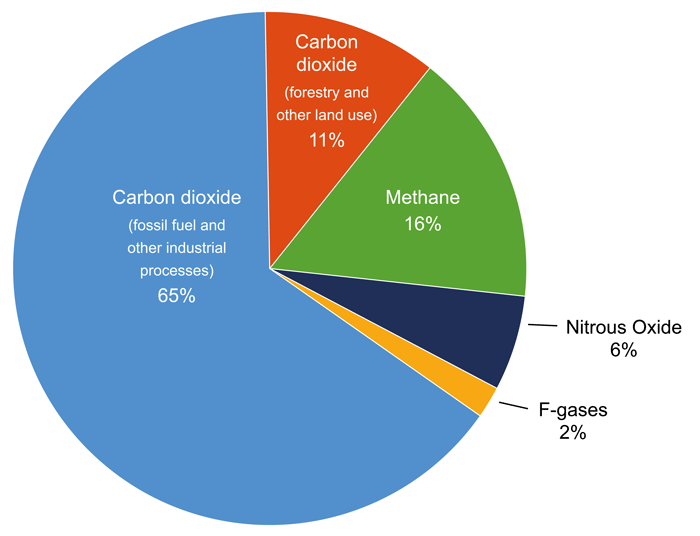
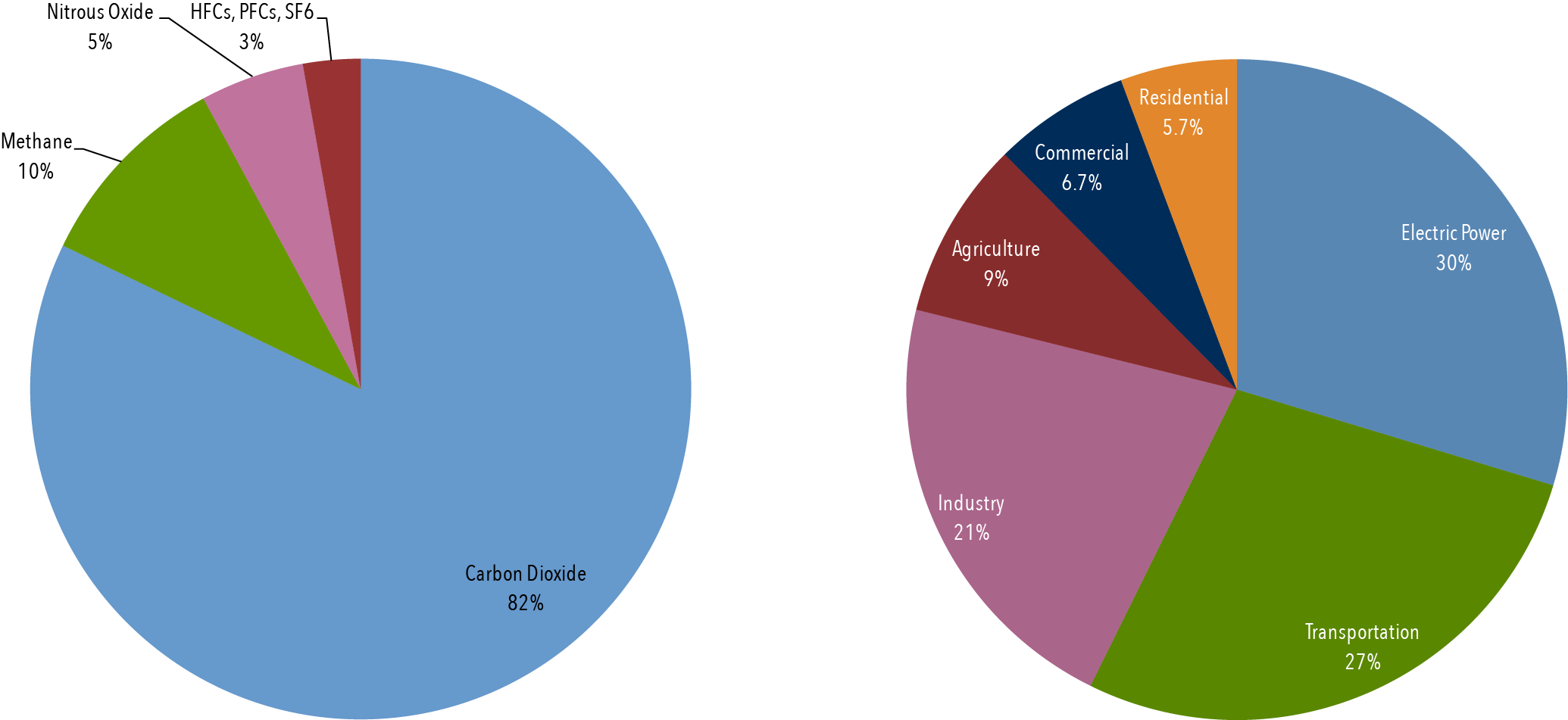
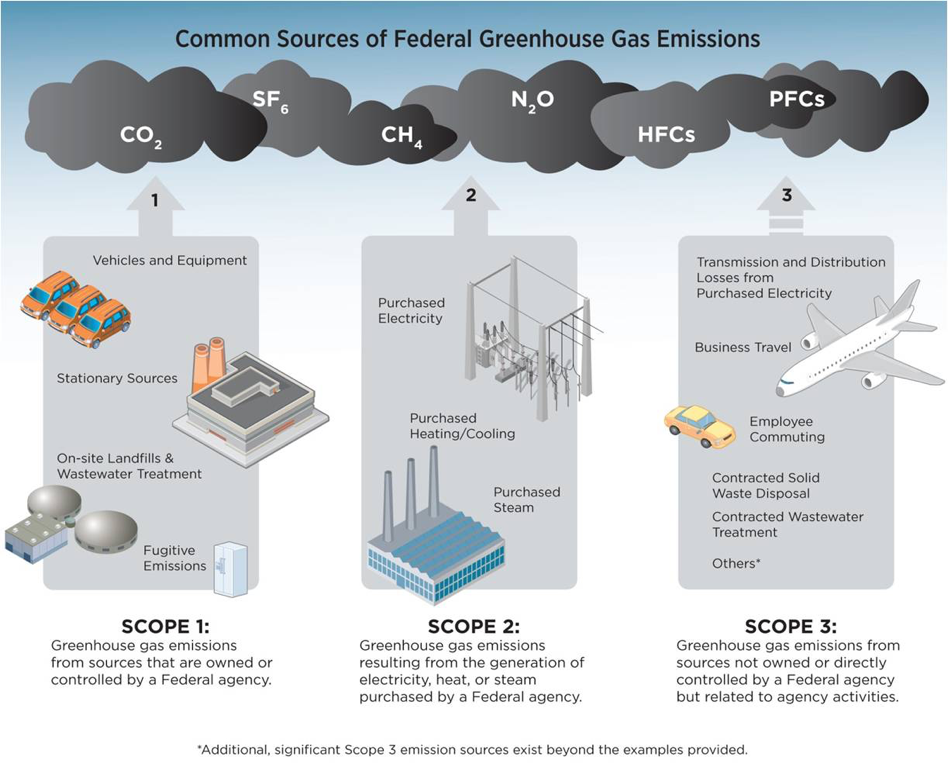
Greenhouse Gases CHAPTER 4 Why some gases are greenhouse gases, but most aren't, and some are stronger than others About Gases The layer model is what is called an idealization of the real world It has the essential ingredient of the greenhouse effect, but it is missing numerous things that are important in the real atmosphereTotal US Emissions in 19 = 6,558 Million Metric Tons of CO 2 equivalent (excludes land sector) Percentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from theViewing diagrams 2 Participate in group brainstorming sessions and class discussions related to the impact of the greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientific process 4 Hypothesize about the effects of global warming on the climate and the world's




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Global Human Green House Gas Emissions By Sector Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions Emissions
7/3/18 Greenhouse gas emissions by sector in the EU According to the fifth assessment report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is extremely likely that human activities over the past 50 years have warmed our planet These activities include for example the burning of coal, oil and gas, deforestation and farmingWhat are the anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the first place?Although the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effectThe enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate changeThis effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount of greenhouse gases




Emissions Of The Powerful Greenhouse Gas Sf6 Are Rising Rapidly World Economic Forum




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
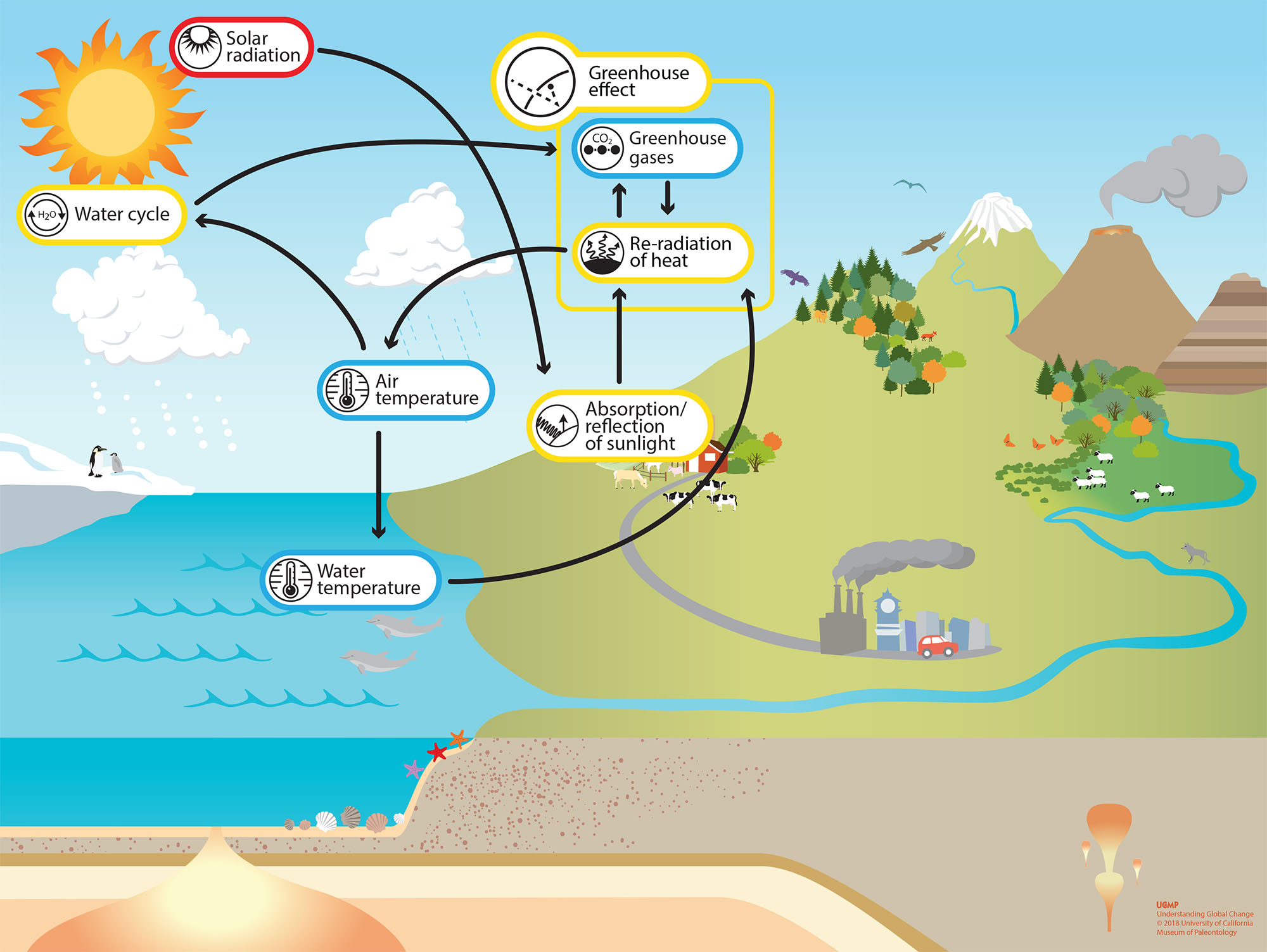
Greenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards space16/7/21 Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth18/5/18 Greenhouse gas emissions affect more than just temperature Another effect involves changes in precipitation , such as rain and snow Over the course of the th century, precipitation increased in eastern parts of North and South America,



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
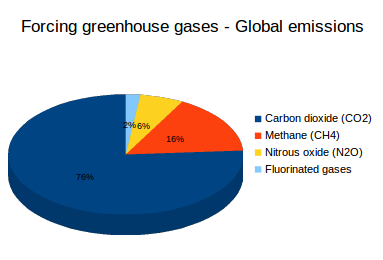
/1/21 Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere15/7/21 The diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surface Some heat escapes into spaceThis chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes
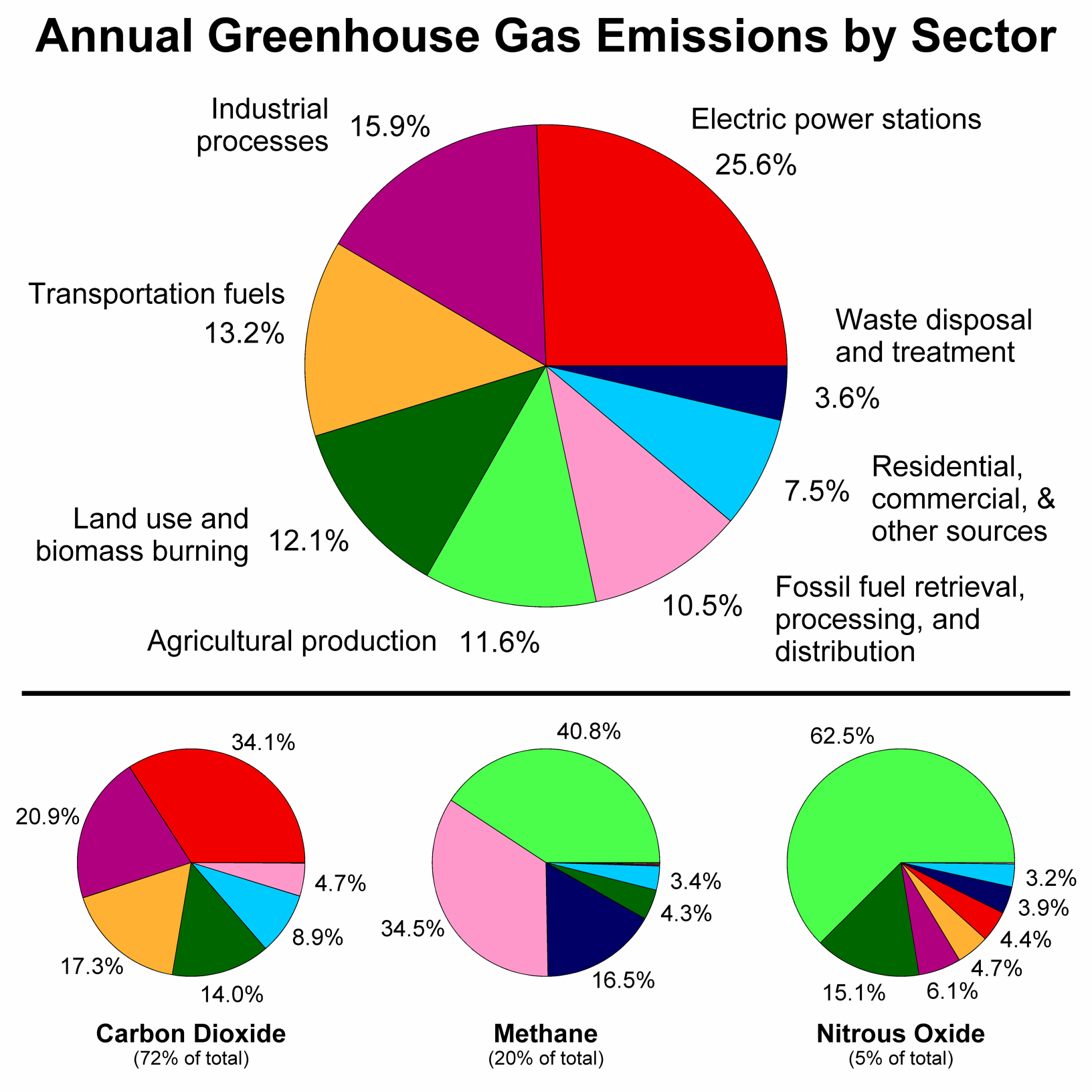



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons
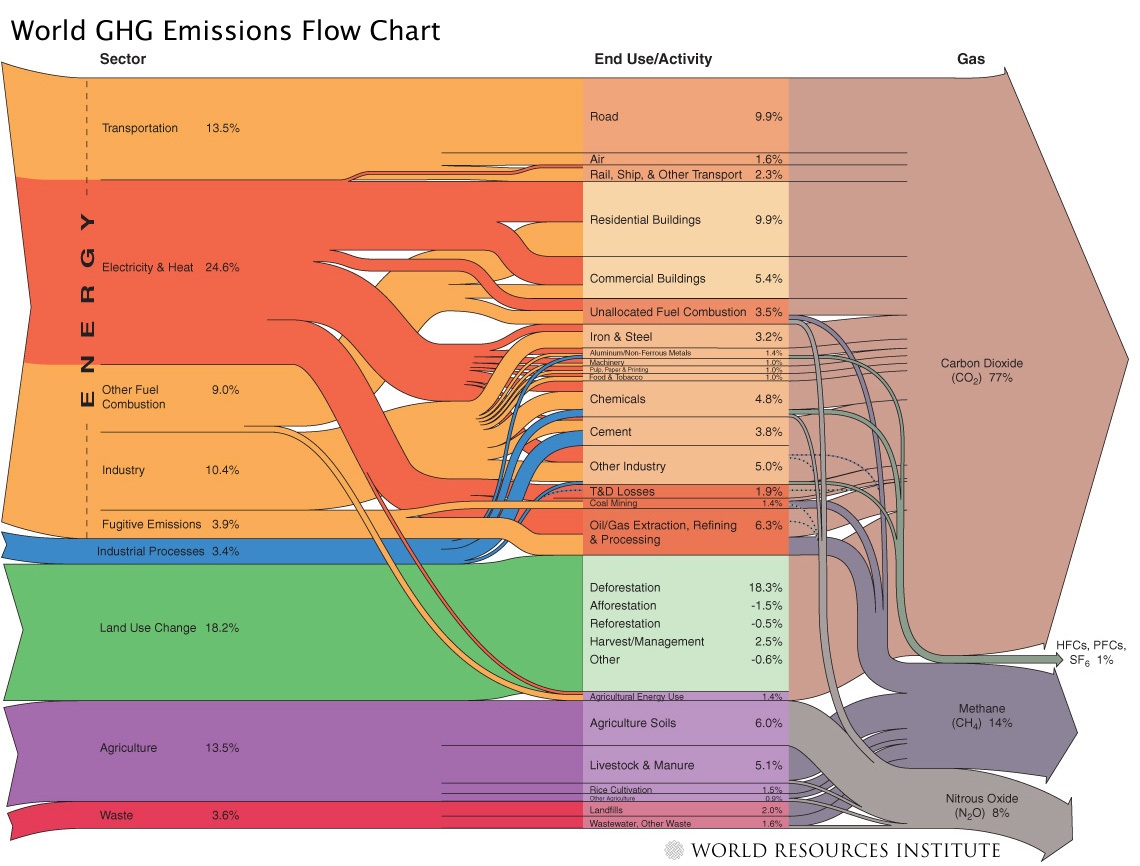



World And Us Ghg Diagrams From Wri Sankey Diagrams
17/8/ The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would beGreenhouse gases Carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide and lowlevel ozone See greenhouse effect Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 08 by Diagram Visual Information Limited Want to thank TFD for its existence?This chart maps out future greenhouse gas emissions scenarios under a range of assumptions if no climate policies were implemented;
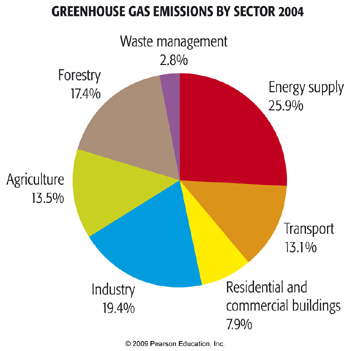



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




Climate Greenhouse Gases Sustainability
The increase of greenhouse gases will, theoretically, enhance the greenhouse effect by trapping more of the heat energy emitted by Earth's surface, thus increasing the surface temperatures on a global scale Scientists expect that the global average surface temperature could rise 145 F in the next 50 years and as much as 10 F in the next centuryThe greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent itTable 25 Key Source Analysis of Greenhouse Gas Emissions for 11, with Land Use, Land Use Change and Forestry Emission Table 26 Greenhouse Gas Emissions for the Years 1994, 00, 05 and 11 Table 27 Greenhouse Gas Emission Indices for Malaysia




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com
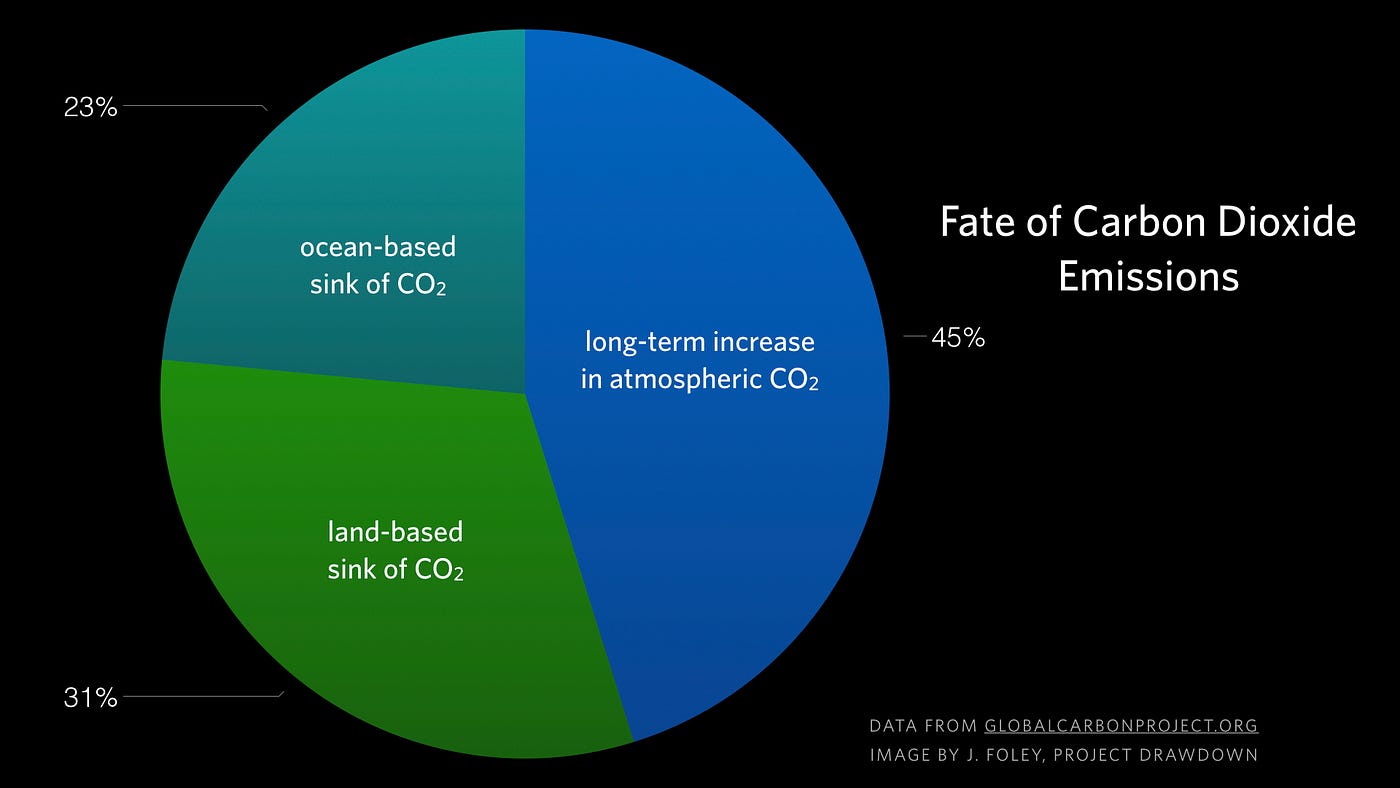
1/6/ Greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric concentrations have increased over the past 150 years Emissions of several important greenhouse gases that result from human activity have increased substantially since largescale industrialization began in the mid1800s9/7/21 Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does notIndeed, the main culprit is, as we might have expected, CO 2 In terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net force




Some Greenhouse Gases Are Stronger Than Others Ucar Center For Science Education



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org
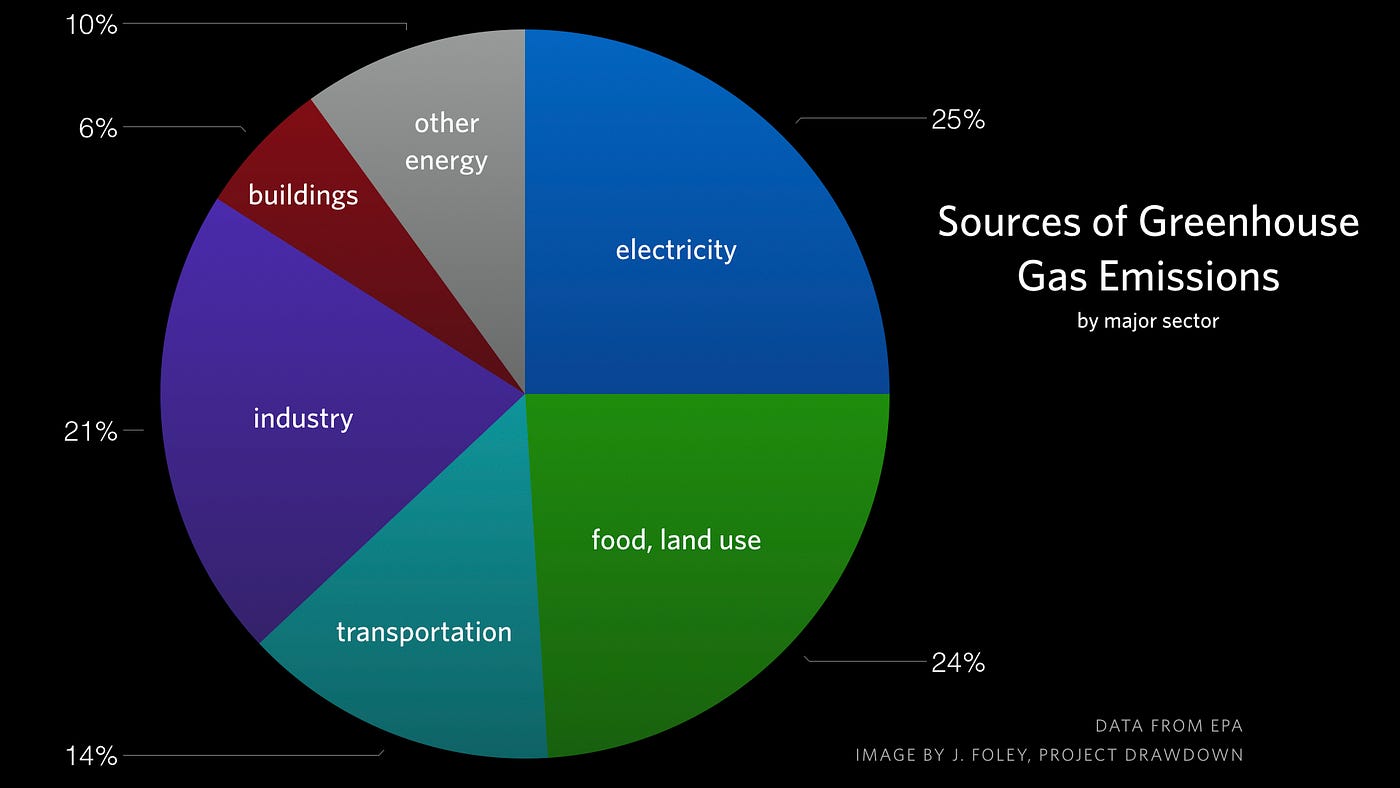
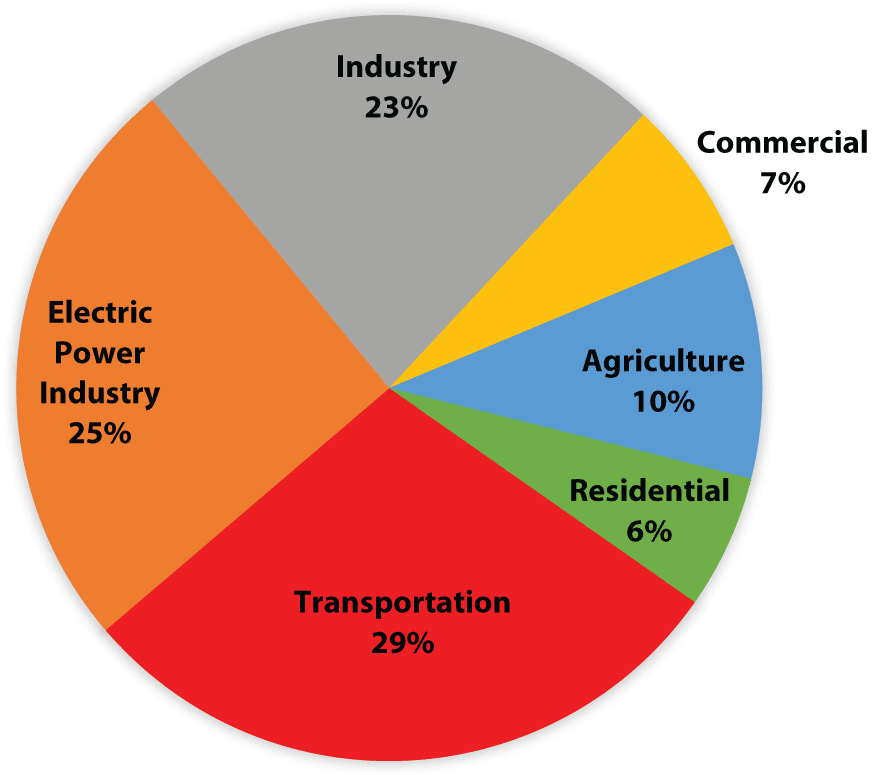
Portion of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States in 14 include transportation (26%) and industry (21%) Figure 3 Diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect The arrows represent radiant energy from the sun entering and leaving Earth's atmosphere Source 'Greenhouse' gases carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, water vapour effectively prevent some of this longwave radiation from leaving the atmosphere;"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone




Percentage Contribution Of Various Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg
WHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of lifeThis warms Earth's atmosphere, making our planet habitable;10/5/21 Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, and




Controlling Industrial Greenhouse Gas Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences the1/6/ Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview Diagram Notes a CO2 emissions related to petroleum consumption (includes 64 MMTCO2 of nonfuelrelated emissions) b CO2 emissions related to coal consumption (includes 03 MMTCO2 of nonfuelrelated emissions)The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but the extra gases produced by human activity are making it stronger We are now adding to these gases faster than oceans and plants can absorb them — the greenhouse effect is being 'enhanced' by humans



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
Greenhouse effect and explore natural and humancaused greenhouse gas emissions and their impacts Students will brainstorm and then research natural and human activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and draw them in a diagram Students then discuss how they can reduce their contributions to greenhouse gas emissions




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament




A Pie Chart Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Ghg 101 Understanding Greenhouse Gases Canada S Oil Sands Innovation Alliance Cosia




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research
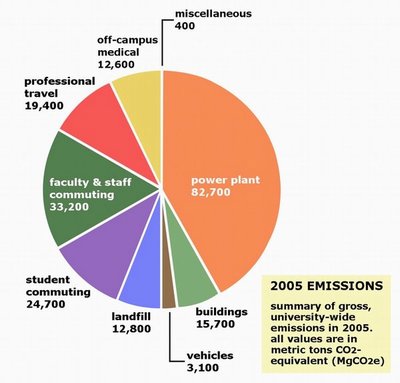



Uw Greenhouse Gases Down 10 Percent From 01 To 05 Inventory Finds Uw News




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
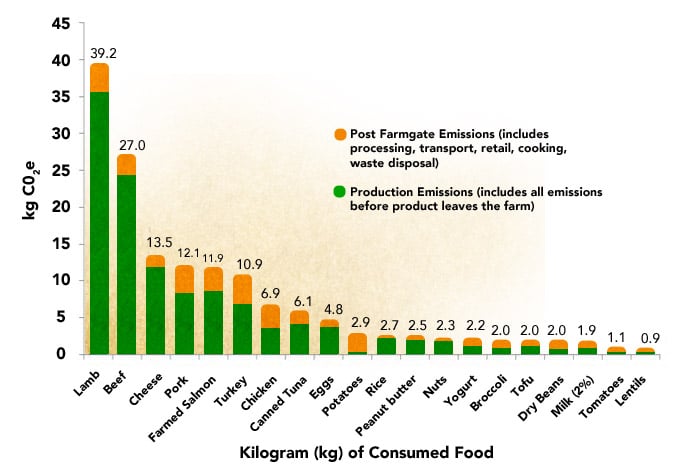



The Impacts 11 Meat Eaters Guide Meat Eater S Guide To Climate Change Health Environmental Working Group




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
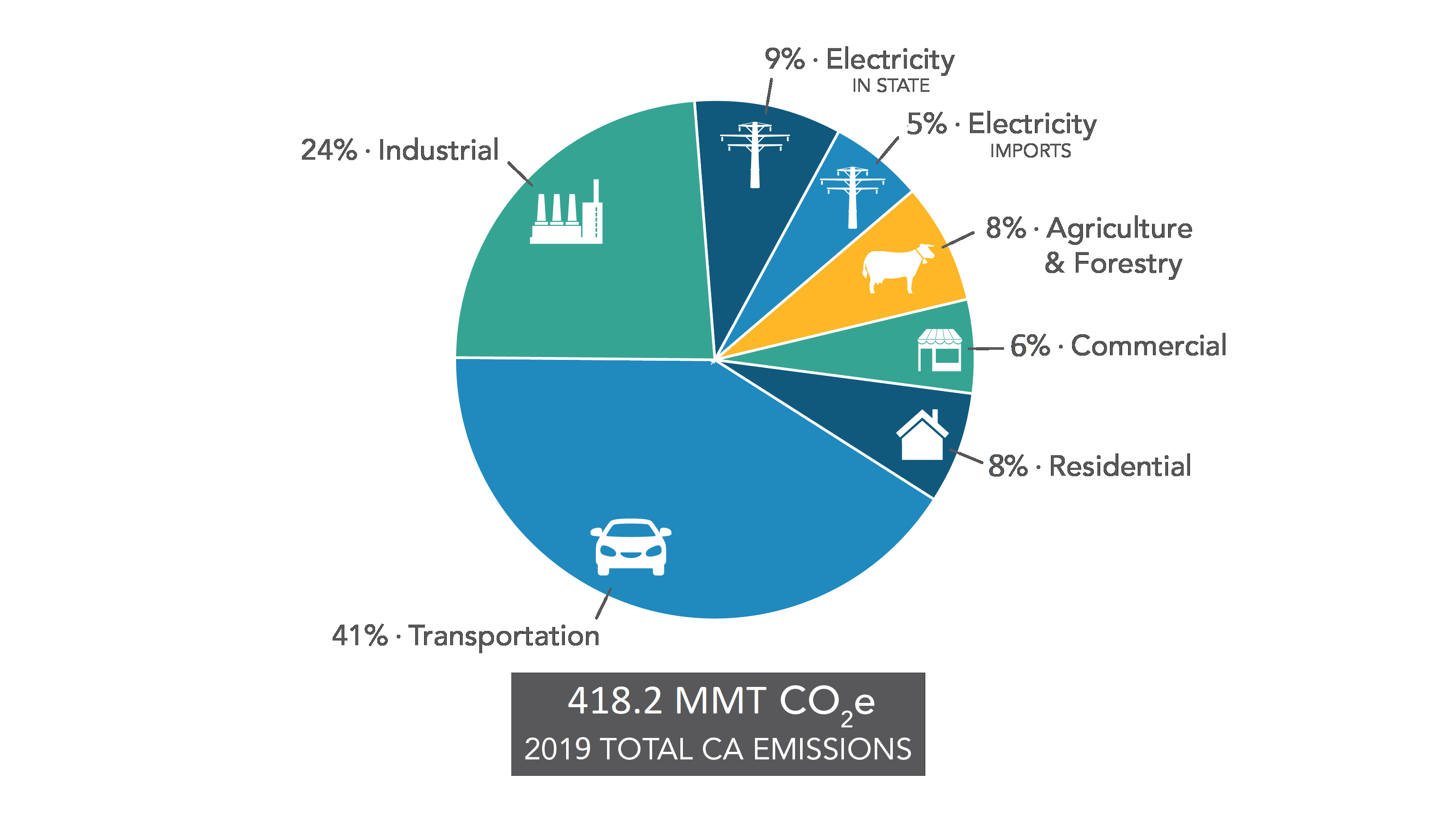



Ghg Emission Inventory Graphs California Air Resources Board




Pie Chart That Shows Country Share Of Greenhouse Gas Emission 30 Comes From China 15 From The Unite Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ghg Emissions



Earthcharts Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector
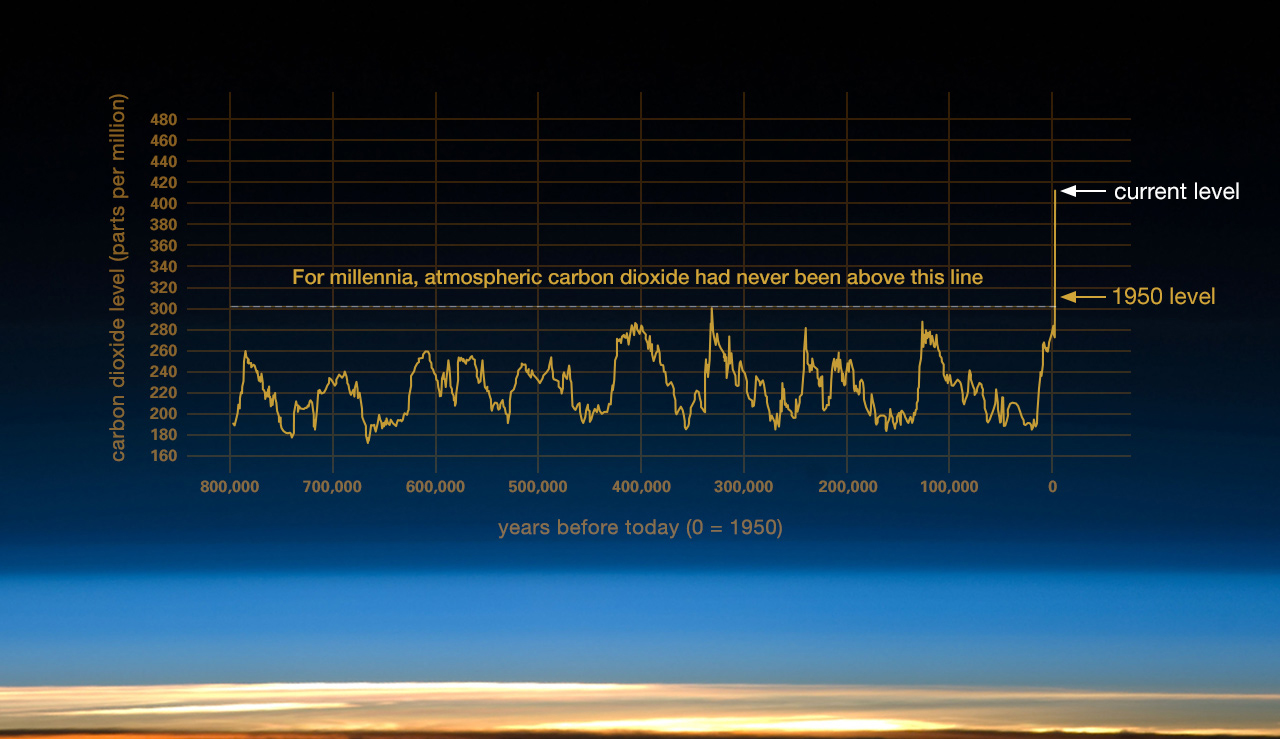



Evidence Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension



1
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Pork Production And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pork Information Gateway




Schematic Overview Of The Main Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Download Scientific Diagram
.png?width=512&name=chart%20(1).png)



Trimble Maps Simplifies Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Tracking And Reporting




Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview



Causes Of Climate Change And Sea Level Rise Coastadapt



Bikes And Walking Transit Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Source




Emissions Sources Climate Central




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Select The Correct Answer The Pie Chart Shows That Electricity Production Emits The Most Greenhouse Brainly Com




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




4 Ways To Cut Plastic S Growing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inside Climate News




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




How To Decarbonize America And The World Techcrunch Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect Artis Energy



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




The Greenhouse Effect World101




How Exactly Does Carbon Dioxide Cause Global Warming You Asked




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




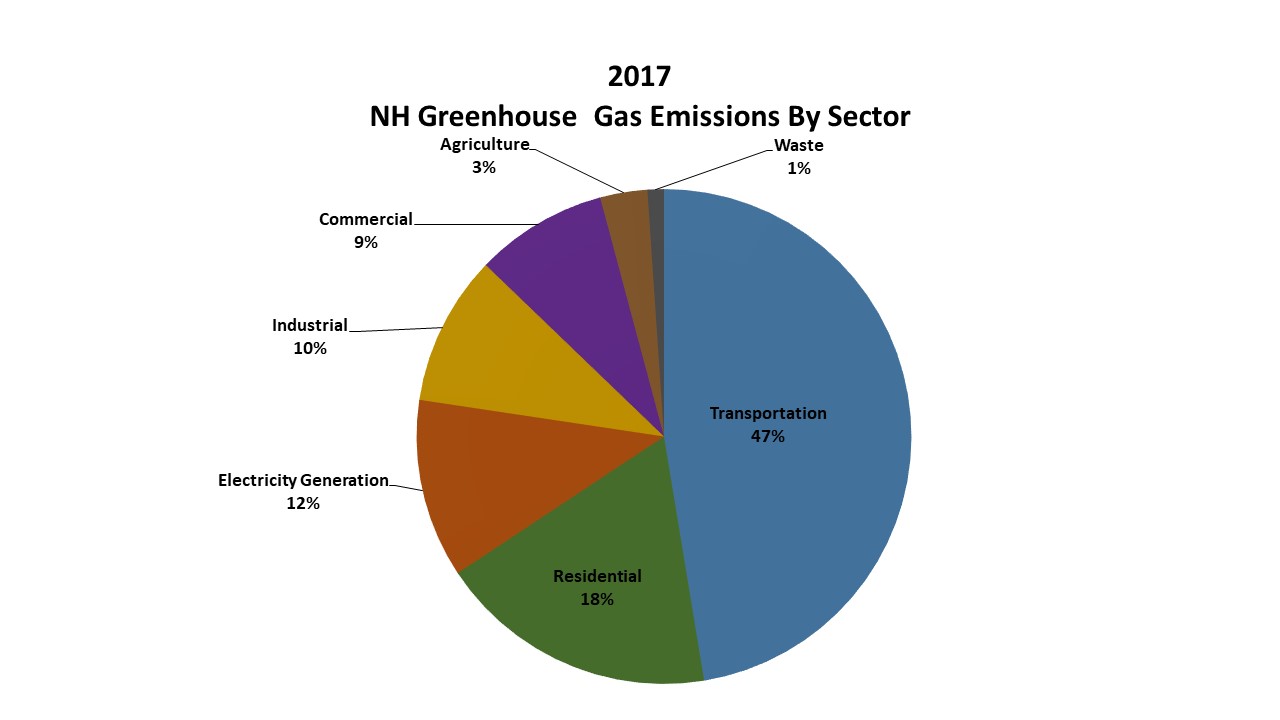
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Emissions Sources Climate Central



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



Greenhouse Gas Reduction Ghg Emissions



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services



1



3




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
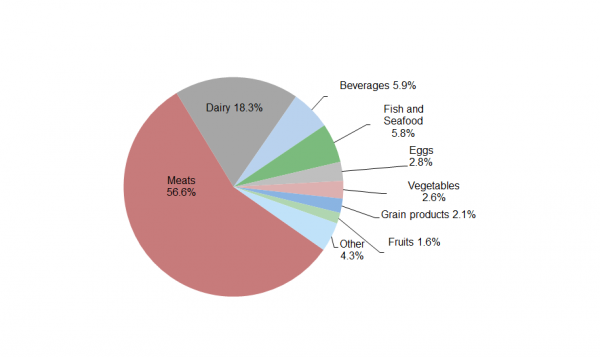



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
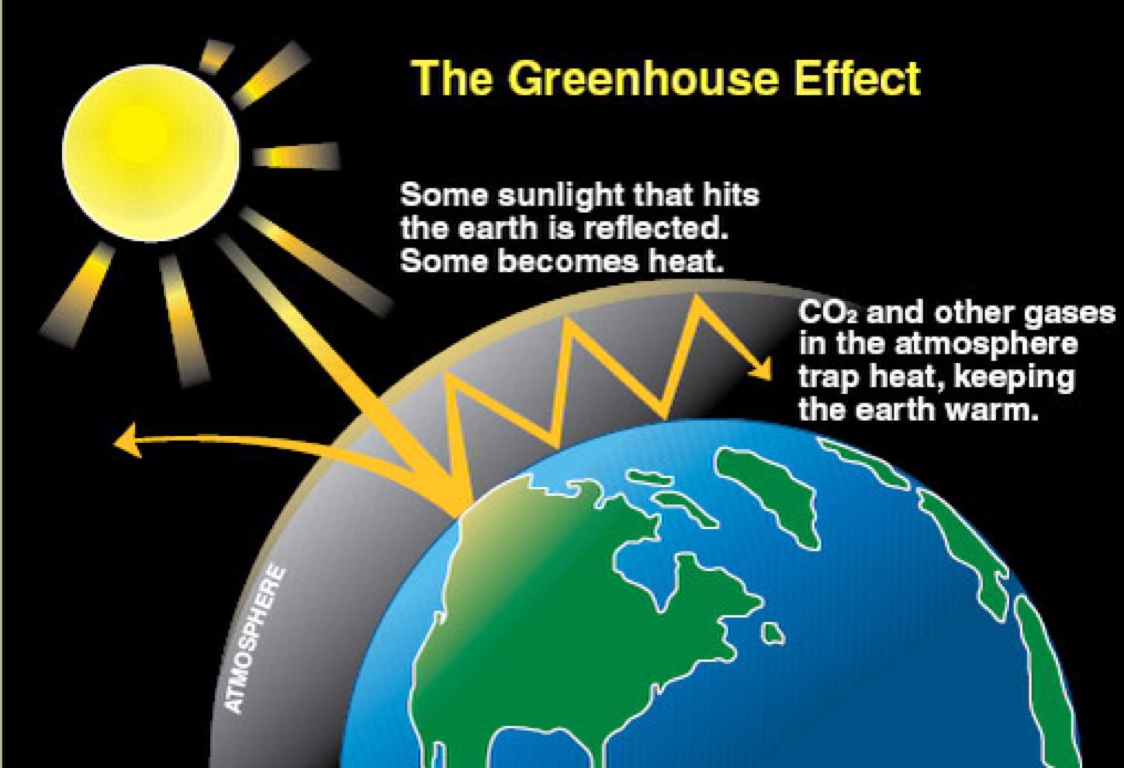



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic
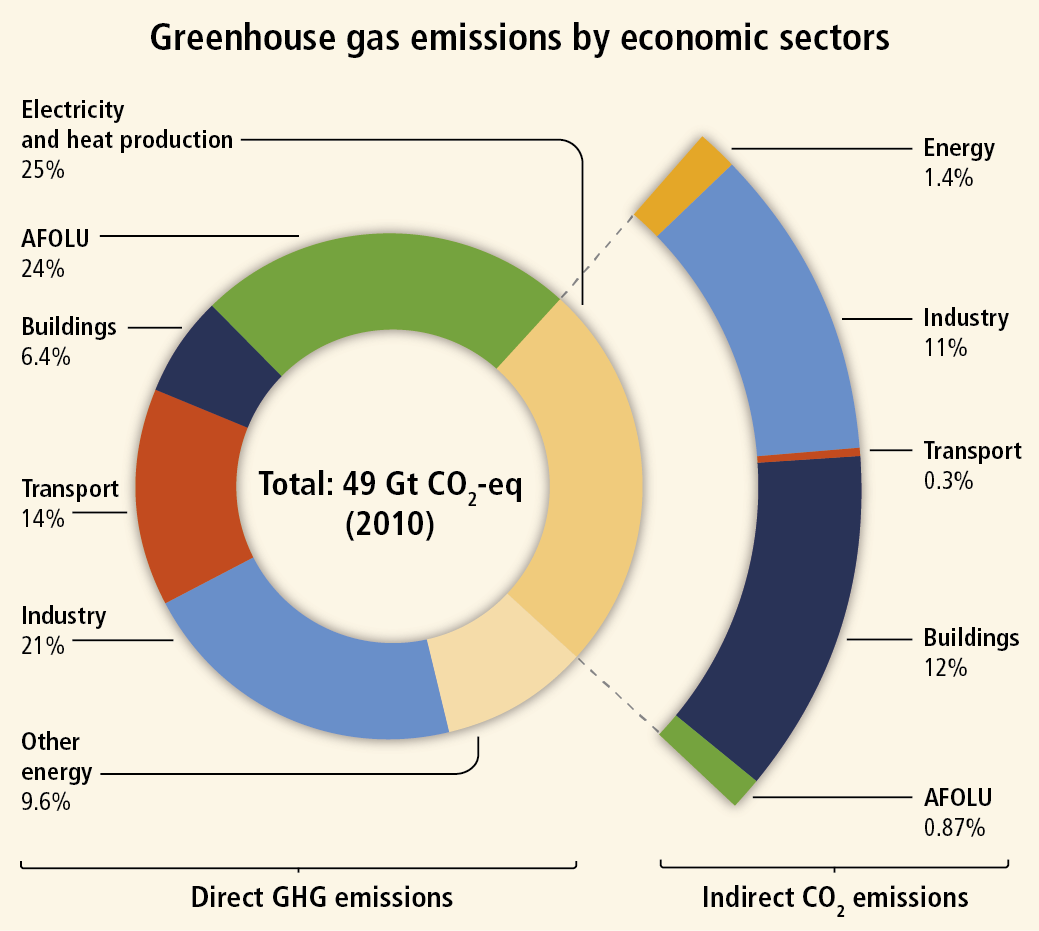



Impact Of Agriculture On Climate Change




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From




Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus
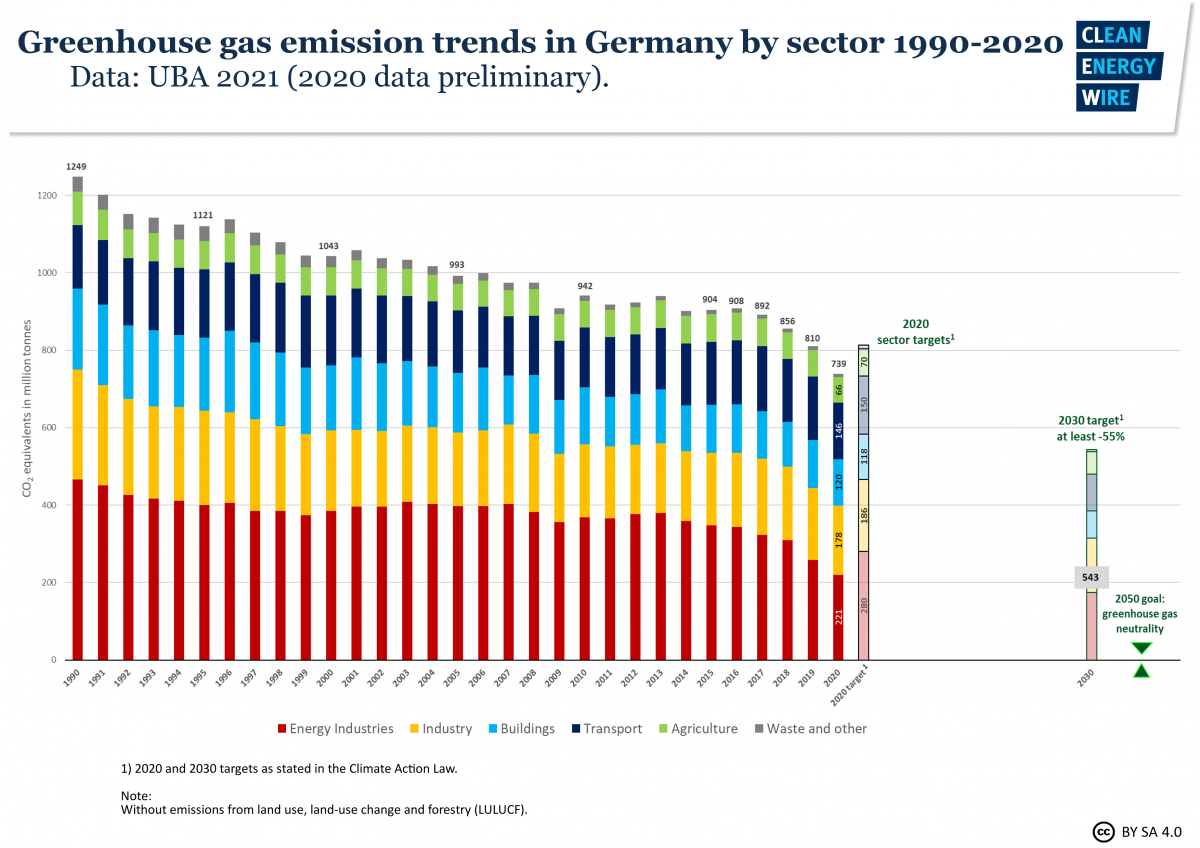



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire
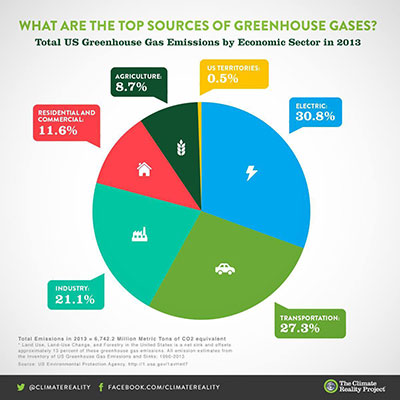



Agriculture Causes Less Emissions Than Transportation




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox
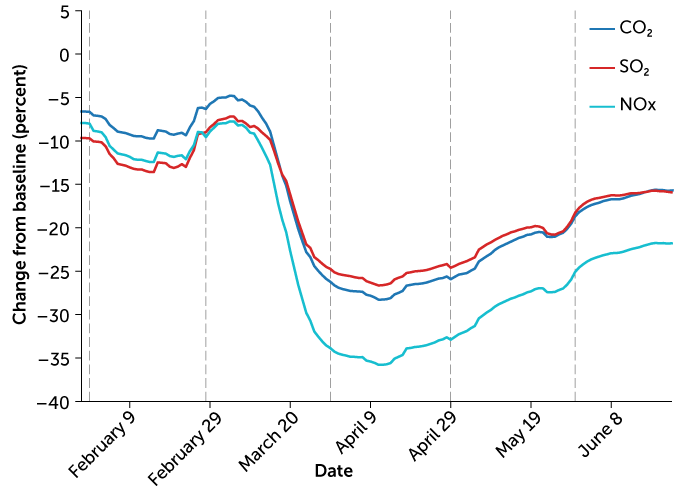



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News
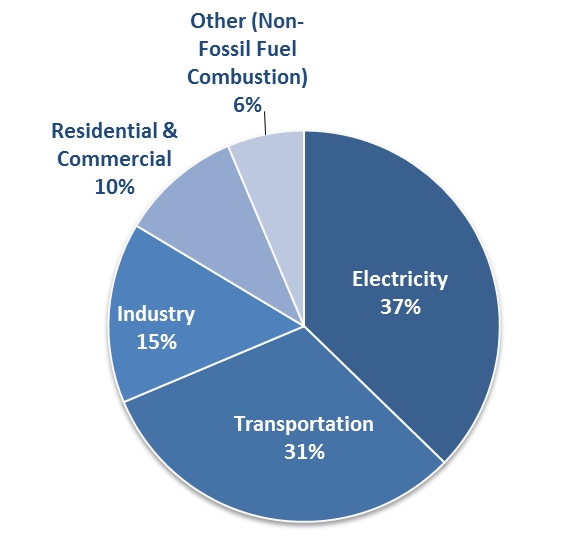



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Matter Of Trust




Italki Ielts Writing Task 1 Answer 22 The Diagram Illustrates How Solar Energy Is Trapped By Greenhouse E



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
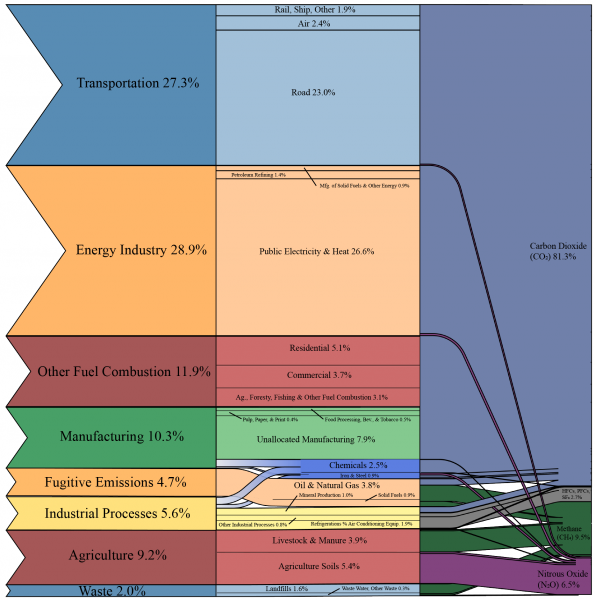



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4250823/ecofys-world-ghg-emissions-flowchart.png)



Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox




Global Gas Emissions Climate Energy And Society College Of Liberal Arts Auburn University




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
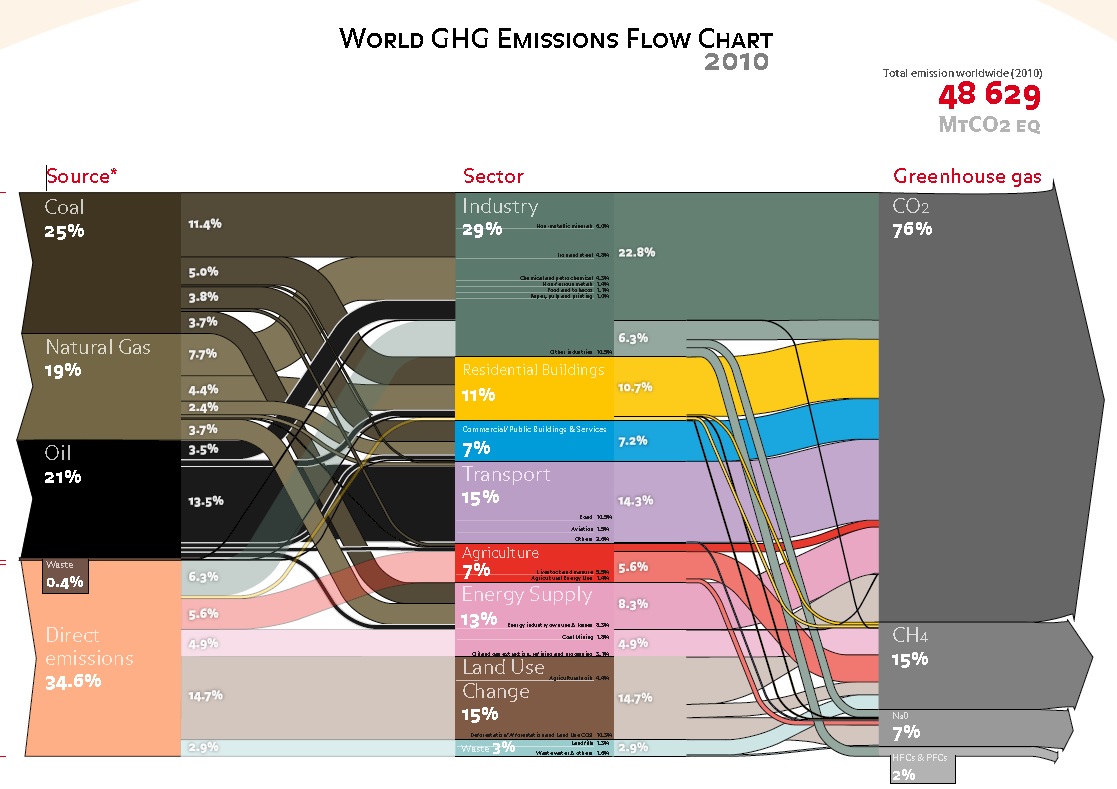



Greenhouse Gases Where They Really Come From Infographic




Nahb Residential Greenhouse Gas Emissions
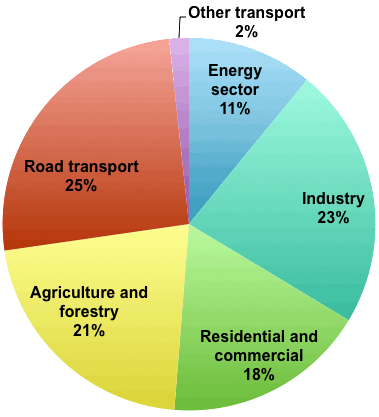



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
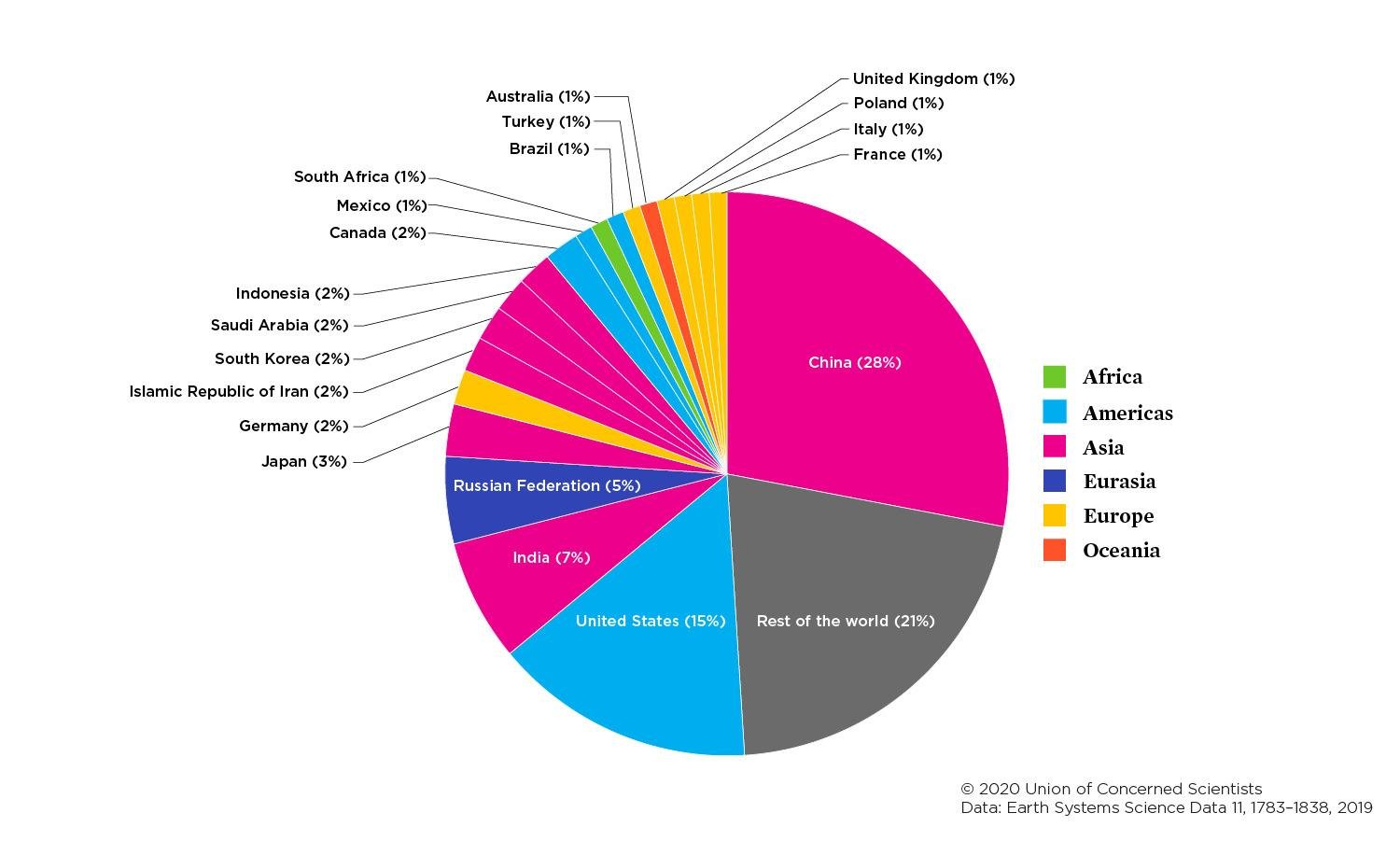



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿